The growth of colonies was observed.
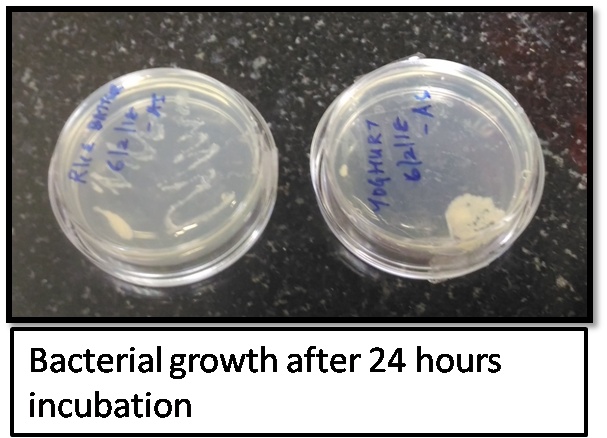
The bacterial colonies was taken from both yoghurt and rice batter (mostly the colonies will be morphologically distinct because the bacterial colonies are from two different sources) were then picked and put into the LB media and aliquots of the bacterial growth was taken once in 30minutes up till 8 hours and one at 24 hours for generating the growth curve by measuring the optical density via Double beam UV visible spectrophotometer (from the facility available at BioNest, Kochi, India).

The optical density was measured at 600nm for both the bacterial colonies grown in yoghurt and rice batter.
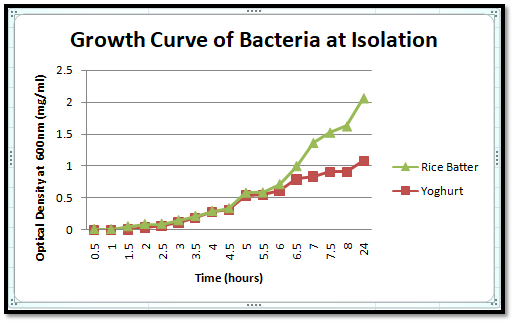
The growth curve of both yoghurt and rice batter in isolation is depicted in the below image.
RESULT:
The growth curve of yoghurt (yellow) has a steady growth till 24 hours, whereas the growth of rice batter bacteria is high initially, and then getting decreased and again raising steadily. This might be because there are 2 different types of bacteria, and the growth of bacteria 1 is inhibiting the growth of bacteria 2 initially, and later, the growth of bacteria 1 started to grow steadily.
Two 14ml test tubes were printed using the Ultimaker 3D Printer available at FABLAB, Kochi in PLA material. I selected PLA as its Biodegradable and bioactive material. One tube was coated with resin for comparing the difference between both the test tubes.

The bacterial culture from yoghurt (culture 1) was then put into LB Broth and poured on the 3D printed test tube, collected aliquots of bacterial growth once in 30min for generating the growth curve.

The growth curve for the bacterial culture in 3D printed test tube is compared with the growth curve for 3D printed tube with resin coating, and with E-coli as negative control, and also compared with the polystyrene control tube.
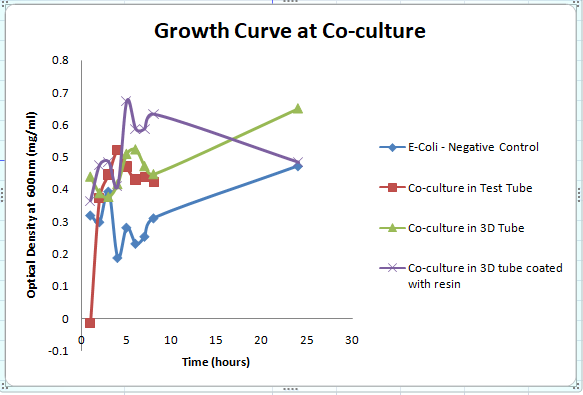
RESULT:
From the above growth curve image, I infer that the growth of co-culture (bacteria from both yoghurt and rice batter) in 3D printed tube made with PLA coated with resin have almost the similar growth as that of E-coli. The co-culture in test tube and that of 3D printed tube without resin coating had a similar growth curve.
COMPARISON OF GROWTH CURVE AT ISOLATION AND CO-CULTURE:
When comparing the growth curve, the growth curve at co-culture was completely different from the growth curve at isolation. The growth at isolation had a steady growth, but in case of co-culture, the growth was unsteady.
Design Assignment
(3a) Design a milli- or micro-fluidic 'artificial gut' or other 'organ-on-a-chip' device to be utilized, at a minimum, for cell culture. Feel free to design your device in 2D-CAD software or vector drawing tool (e.g. Adobe Illustrator, AutoCAD) or 3D design tool (e.g. Rhino, SolidWorks).
(3b) Fabricate your device, or at least one component of your device. Document the following aspects of fabrication and function in your class page:
- What features of your organ are you attempting to emulate?
I am attempting to emulate the function of urinary bladder, controlling the urine from the ureters in case of stress incontinence in women and aged population.
- How is your device intended to function?
The posterior tibial nerve and sacral nerve are responsible for holding the urine, and sends signal to brain to urinate. The device would have the function of sending electrical simulation to these nerves via a vaginal or anal electrode, which stimulates the nerves to treat the incontinence. This type of electrical stimulation is under research for treating especially women with incontinence.
- Were you able to fabricate your device? Which components? Which parts 'worked' and which ones didn't?
I will attempt to fabricate the device with a transparent moulding and casting, atleast the part for electrical stimulation of the bladder through an electrode in vagina or anus.
- What will you aim to improve for your next iteration of design + build?
I will get in touch with a urologist to get more clarity about the electrical simulation and then, think about how to iterate the next version of my device.
(3c) Culture the organism from (1) in your milli- or micro-fluidic device. Run a negative control in a device with liquid media only. Collect the liquid culture from your device (+/- bacteria) and plate in the presence of an antibiotic. Report colonies for the +/- experiments.
In the process of fabricating the device, to be updated after the experiment.
(4) Share your device designs on 'Metafluidics' (www.metafluidics.org), including Bill of Materials, assembly instructions, and any associated hardware. Irrespective of how far you get in (2), please share your latest iteration! You can always update your device later.
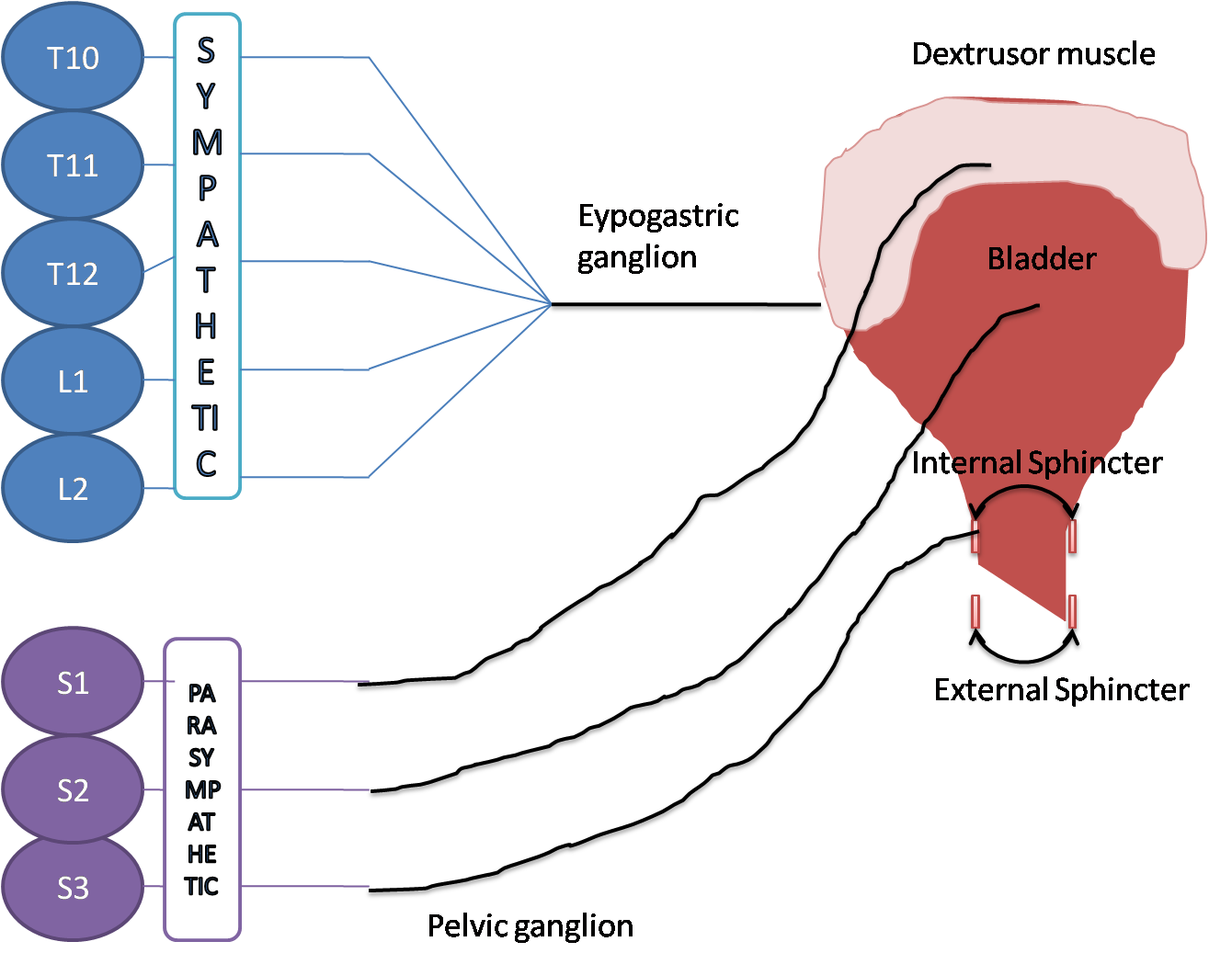
The schema based on how the device will be fabricated is given in the below image:
Background reading :
The lower urinary tract (LUT), including the urinary bladder, urethra, and periurethral striated muscles, serves two important roles: continence, the storage of urine in the bladder, and micturition, efficient voiding of urine from the bladder at an appropriate time. These functions are controlled by neural circuits in the spinal cord, brainstem, and higher centers, and engage the sympathetic (hypogastric nerve), parasympathetic (pelvic nerve), and somatic (pudendal nerve) nervous systems. The bladder and urethral sphincters are controlled in a reciprocal manner to accomplish the two primary functions of the LUT. During storage, urine is retained in the bladder because the sympathetic pathway is activated, producing bladder relaxation via adrenergic signaling through the hypogastric nerve, and activation of the somatic pudendal nerve output from Onuf's nucleus produces coordinated contraction of the external urethral sphincter (EUS).The initiation of voiding occurs when the parasympathetic pathway is activated, producing contraction of the detrusor muscle in the bladder via cholinergic excitation through the pelvic nerve and the urethral sphincters are relaxed, allowing urine to leave the bladder and flow through the urethra.
During bladder filling, afferent fibers in the pelvic and hypogastric nerves deliver information from mechanoreceptors sensitive to pressure and stretch, or increases in tension of the bladder wall, signaling bladder distention to the sacral and lumbar levels of the spinal cord, respectively. The pudendal nerve (PN) also contains afferent nerves; the dorsal genital nerve (dorsal nerve of the penis – DNP) is well documented in humans, and other smaller sensory branches have been identified in animals, such as the cranial sensory nerve (CSN) in cats. These somatic fibers provide sensory input from the pelvic floor, urethra, and external genitalia to the sacral spinal cord and play a role in mediating pudendo-vesical reflexes that can impact continence and micturition by providing negative (guarding reflex) or positive feedback (augmenting reflex) during urine flow in the urethra. After entering the dorsal horn, the afferents diverge; some fibers make projections in the dorsal horn to local interneurons and some send long ascending projections to the periaqueductal gray (PAG) and pontine micturition center (PMC).
The PMC plays a critical role in the regulation of continence and micturition, and switching circuitry located between the PAG and PMC integrates the ascending afferent signals and descending commands from higher brain centers to direct the transition from continence to micturition that is executed by the PMC. Chemical or electrical stimulation of the PMC produces voiding that is very similar to reflex micturition,indicating that the PMC is a critical center for micturition. Descending signals from the PMC produce excitation of the sacral parasympathetic nucleus (SPN), causing bladder excitation and an increase in bladder pressure, and inhibition of Onuf's nucleus (the pudendal motor nucleus) to produce relaxation of the external urethral sphincter (EUS), allowing urine to flow [1]
New ethics or safety considerations this week:
Do your activities this week raise new ethics and/or safety considerations you had not considered in week 1? Describe what activities have raised these considerations and any changes you have implemented in response.
- In this week's assignment, I learnt how to work with Biosafety cabinet. When I worked with the bacterial cultures inside the hood, I learnt how to handle the reagents within the hood and how to prepare cotton plugs tight before autoclaving.
REFERENCES
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4397195/
Go back to home page